At the beginning of May, Ahmet has published a really interesting article Run Privileged Functions With Non-Admin Users which I highly recommend as I believe you could have so many applications for this to reduce admin dependency.
At the same time the above was published I was presented a small challenge where a SmartPush which was run on a webform as part of a groovy rule was only pushing some of the data, specifically only the entities that the user would have access to.
The problem is that in this process, the user would “transfer/allocate” data between entities using a Entity and a Target Entity dimension, members prefixed with a “E_” or “TE_” respectively. The user would have access to specific access to the Entity dimension, and full access to the TE dimension.
Without going into too much detail, using a Groovy rule on a web form, the rule would take the entered data against the Entity and Target Entity selected, which would mean that opposite entries show up in both entities. Simple so far right?
At the end of the groovy rule it then runs a smartpush from source cube to target cube. Still nothing wrong?
Actually, the issue arises when the user has no access to the entity where they have calculated an opposite entry. While the transfer of data would have completed in the source cube and nets off to zero, the smart push to the report cube would have only pushed one side of the data for the entity that the user is provisioned for.
Unfortunately the user would sometimes be unaware that only half the data has been pushed to the target cube as no error was presented.
The solution? To run the smartpush as a privileged user/admin.
- update the existing groovy rule to exclude the final step of executing the create datamap (smartpush) operation. This rule now becomes the “wrapper rule”
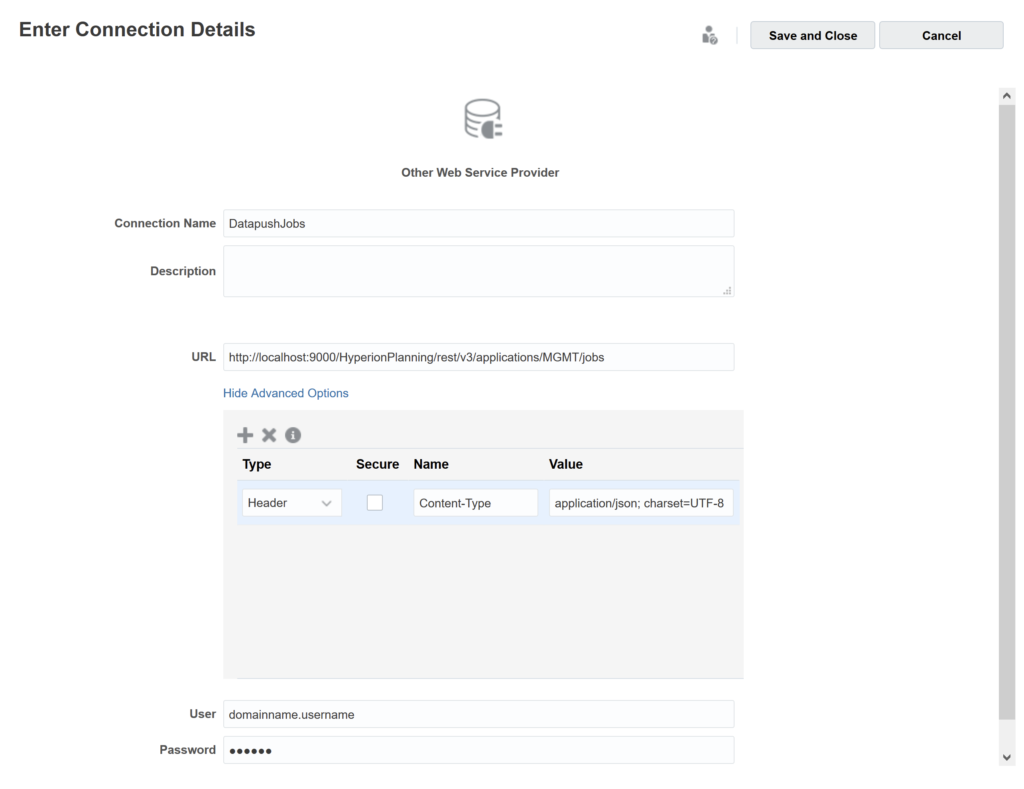
- Create a local connection object in your application
- add new ‘string’ type run time prompts
- In the existing “wrapper” groovy rule, populate the RTPs with the string generated for edited cells
- In wrapper rule, create a http request using the connection created with admin privileges in step 2 to run the body rule.
- create a new body rule which contains a modified smartpush operation using the RTPs as parameters
Step 1 has to do with the existing rule that includes the datamap execute command, this will need to be removed and readded to a “body” rule in Step 5, I won’t go too much into detail for this as in this particular scenario it has to do with capturing the edited cells in the form that will be used as parameters on the intersection of data to be pushed.
Step 2, is to create a local conection object in your application, this will require admin user credentials as that will have access to all all entities, typically an account that is used for admin automations like epmautomate jobs.
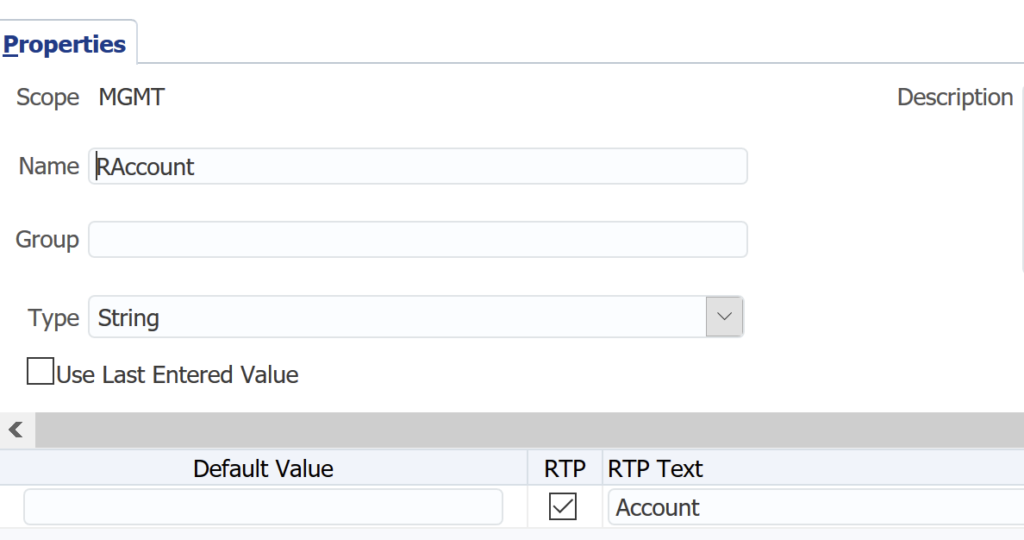
Step 3, add the RTP strings for the members you wish to specify in your datamap execution of the push, one example shown below;
Step 4, edit in existing groovy script and after the string members are complete for edited cells, define params amd body as a JSONObject and put the string members collated from the edited grid cells part to the relevant RTP.

Step 5, add the http request using the getConnection command to run the body rule (created in the next step).

Additionally as Ahmet explains in his earlier article that you can return a host of information regarding the HttpResponse and the job can return information on it’s successful run. Please see the article for details on this, Run Privileged Functions With Non-Admin Users
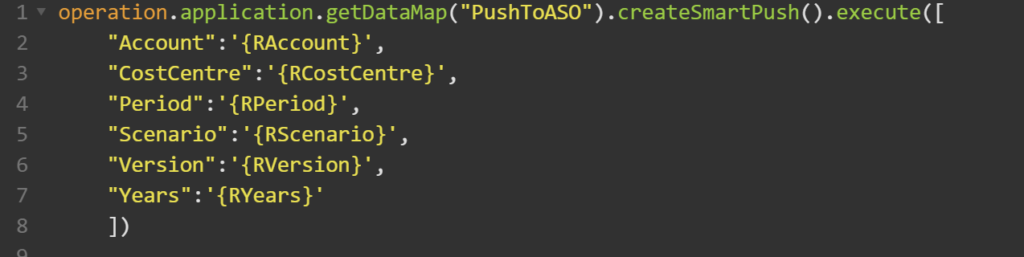
Step 6, Create the body rule with the createSmartPush().execute() option passing the parameters that we put together in def Params using the RTPs.
Step 7, Just kidding, we’re done. No more incomplete datamap Smartpushes due to restricted dimension access.



